
Eastern Michigan University Eastern Michigan University
DigitalCommons@EMU DigitalCommons@EMU
Senior Honors Theses and Projects Honors College
2024
A 6nancial economic analysis of Amazon A 6nancial economic analysis of Amazon
Rebekah Arcilla
Follow this and additional works at: https://commons.emich.edu/honors
Part of the Economics Commons

A 6nancial economic analysis of Amazon A 6nancial economic analysis of Amazon
Abstract Abstract
This analysis values Amazon (AMZN) as it relates to prospective investors through a 6nancial and
economic lens. It provides an investment recommendation using various methodical analyses: Porter 5
Forces Framework, 6nancial statement analysis, economic analysis, and a review of the company. The
Porter 5 Forces Framework identi6es key forces within Amazon’s industry that could result in negative or
positive impact. The 6nancial statement analysis measures the 6nancial health and capability of the
company. The economic analysis analyzes the current state of the economy and its effect to Amazon.
The review of the company reveals signi6cant risks that create undesirable performance of Amazon’s
stock price. Major 6ndings were that Amazon holds promising ability to generate future cash 7ows from
operations and minimize the impact of losses from unsuccessful operations. The United States economy
is found to be in a current state of recession. The investment recommendation highlights important
suggestions for the investor.
Degree Type Degree Type
Open Access Senior Honors Thesis
Department or School Department or School
Economics
First Advisor First Advisor
Christopher Elias, Ph.D.
Second Advisor Second Advisor
Amanda Stype, Ph.D.
Third Advisor Third Advisor
Peter Higgins, Ph.D.
Subject Categories Subject Categories
Economics
A FINANCIAL ECONOMIC ANALYSIS OF AMAZON
By
Rebekah Arcilla
A Senior Project Submitted to the
Eastern Michigan University
Honors College
In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Graduation
with Departmental Honors in Quantitative Economics
Approved in Ypsilanti, MI on April 15, 2024
Project Advisor: Christopher Elias, Ph.D.
Departmental Honors Advisor: Amanda Stype, Ph.D.
Department Head: Peter Higgins, Ph.D.
Dean of the Honors College: Ann R. Eisenburg, Ph.D.
1
Table of Contents
ABSTRACT'.................................................................................................................................................................................'2!
PURPOSE'OF'PAPER'...............................................................................................................................................................'2!
HISTORICAL'BACKGROUND'................................................................................................................................................'3!
PORTER'5'FRAMEWORK'......................................................................................................................................................'4!
THREAT&OF&ENTRY#.........................................................................................................................................................................................#4!
COMPETITION&IN&INDUSTRY#..........................................................................................................................................................................#5!
THREAT&OF&EXISTING&SUBSTITUTES#............................................................................................................................................................#5!
POWER&OF&SUPPLIERS&AND&BUYERS#............................................................................................................................................................#6!
FINANCIAL'STATEMENT'ANALYSIS'...................................................................................................................................'6!
WEIGHTED&AVERAGE&COST&OF&CAPITAL#.....................................................................................................................................................#6!
DISCOUNTED&CASH&FLOW&MODEL#...............................................................................................................................................................#9!
SENSITIVITY&ANALYSIS#...............................................................................................................................................................................#11!
FINANCIAL&RATIOS#......................................................................................................................................................................................#11!
ECONOMIC'ANALYSIS'..........................................................................................................................................................'13!
GDP&GROWTH#..............................................................................................................................................................................................#14!
INFLATION#....................................................................................................................................................................................................#15!
INTEREST&RATES#..........................................................................................................................................................................................#15!
UNEMPLOYMENT#.........................................................................................................................................................................................#16!
STATE&OF&ECONOMY#....................................................................................................................................................................................#16!
MACROECONOMIC&RISKS#............................................................................................................................................................................#17!
REVIEW'OF'COMPANY'........................................................................................................................................................'18!
EVALUATION&OF&MANAGEMENT#................................................................................................................................................................#18!
KEY&RISKS#.....................................................................................................................................................................................................#19!
NORTH&AMERICAN&SEGMENT&RISKS#.........................................................................................................................................................#20!
INTERNATIONAL&SEGMENT&RISKS#.............................................................................................................................................................#20!
AWS&RISKS#...................................................................................................................................................................................................#21!
LEGAL&RISKS#.................................................................................................................................................................................................#21!
CONCLUSION'..........................................................................................................................................................................'22!
INVESTMENT&RECOMMENDATION#.............................................................................................................................................................#22!
WORKS'CITED'.......................................................................................................................................................................'23!
2
Abstract
This analysis values Amazon (AMZN) as it relates to prospective investors through a
financial and economic lens. It provides an investment recommendation using various
methodical analyses: Porter 5 Forces Framework, financial statement analysis, economic
analysis, and a review of the company. The Porter 5 Forces Framework identifies key forces
within Amazon’s industry that could result in negative or positive impact. The financial
statement analysis measures the financial health and capability of the company. The economic
analysis analyzes the current state of the economy and its effect to Amazon. The review of the
company reveals significant risks that create undesirable performance of Amazon’s stock price.
Major findings were that Amazon holds promising ability to generate future cash flows from
operations and minimize the impact of losses from unsuccessful operations. The United States
economy is found to be in a current state of recession. The investment recommendation
highlights important suggestions for the investor.
Purpose of Paper
Following the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a heightened
awareness in personal wealth and investments. Many closely follow the volatility in the market
and seek opportunities for exponential gain. While many companies’ stock prices were hit hard
through economic recession, there were few that were hardly hit. Among these are the
technology companies and healthcare companies that found great benefit from the stay-at-home
mandates. Amazon is one of the companies that saw a rapid increase as consumers flocked to e-
commerce, cautious of leaving the safety of their households. As the economy begins to return to
pre-pandemic “normalcy,” how will Amazon’s stock price be affected? Using a discounted cash
3
flow model and analyzing various risks, this analysis seeks to find a current investment position
for Amazon’s stock.
First, I will provide a historical background on the company of Amazon. Next, I will
discuss strengths of Amazon using the Porter 5 Framework, a financial metric used to identify
competitive forces within an industry. This will be followed by an analysis of Amazon’s
financial statements to understand its impact on investors. Lastly, I will provide an economic
analysis to recognize any potential business risks for potential shareholders.
Historical Background
The rise of Amazon can be attributed to its founder Jeff Bezos. He began his career
working in Wall Street at the hedge fund DE Shaw. Through this position, he was tasked with
keeping up to date on what new businesses are doing. It was in this role that he realized the
untapped potential of the Internet and the power in using data in the business model. He took on
the risk of opening up his own e-commerce business, moving to Seattle with his wife to open up
Amazon in July of 1995. This website took its name from Earth’s largest river adapting its
meaning to be gigantic. Bezos devised and executed a business model that was the first of its
kind. His focus was on selling only books: a category that had the greatest variety of inventory
among any other category in a retail store. A huge selection and convenience was right at the
customer’s fingertips. Books became the catalyst that jump started Amazon into becoming a
household name.
The customer was always at the forefront of the business model. Company culture was
built around a customer obsession, always holding empathy for meeting their needs above all.
And through the use of data, Amazon was able to finetune their website to cater better to serving
4
their customers. All customer behavior was tracked and used to predict what books they would
enjoy that they weren’t aware of. This is another area where Amazon became a pioneer in the
kind of power the internet can hold. Data analytics has served and continues to be one of the key
factors in the dominance of this company (Frontline PBS).
In its early start, Amazon was not profitable. It operated at a loss for nearly the first 10
years of its existence. This did not stop Bezos from reaching out to investors, asking them to
place their bets on the bright future Amazon holds. He was upfront that investors would not see
net positive returns for many years. But Amazon held the ability to build a firm infrastructure
that will create huge opportunities for upscaling the business. They made the conscious decision
to gain market share rather than finding ways to be profitable quicker (Frontline PBS).
Porter 5 Framework
The Porter 5, developed by Michael Porter, is framework that allows one to recognize a
company’s competition within its industry and its drivers behind economic value (Harvard
Business School). For investors, it is important to understand what threats exist in the industry
that could decrease Amazon’s current market share. It is also beneficial to use this framework to
understand financial success and longevity of the company.
Threat of Entry
Amazon remains a dominant force that is preventing new sellers from entering the
industry. While there has been an increase in direct-to-consumer websites, the initial capital and
investment required to start has created a barrier for new entrants. Amazon has strategically
utilized economies of scale to their advantage in building their platform. Third party sellers are
independent brands or companies that pay a service fee to sell their products through Amazon.
5
These sellers also see an increase in conversion rates, a consumer deciding to purchase a product
after viewing it, when utilizing Amazon’s Prime logistics (Amazon Annual Report 6). For
Amazon Web Services (AWS), the cloud computing space is primarily taken up by the “tech
giants.” Microsoft, Google, IBM, and Oracle are few of the companies that have the most market
share. This industry has extensive barriers to entry given the large amounts of initial required
capital investment.
Competition in Industry
Amazon faces fierce competition as they are a company involved in many different
industries. For the sake of this analysis, the main focus will be on the biggest competitors in their
operational segments: AWS, North America, and International segments.
In person retail shopping still remains one of Amazon’s biggest competitors for the North
America and International segments. Consumers still hold a preference for physical stores and
shopping centers, despite the spike in demand for online shopping. These brick-and-mortar
retailers also maintain a customer brand loyalty and long-standing history. Chinese company
Alibaba Group is another large competitor for Amazon’s e-commerce globally, and cloud
computing in China. This company has looked to attract international sellers on its platform with
lower fees. As mentioned previously, AWS competes for market share among other technology
companies such as Microsoft, Google, and IBM. In 2019, Microsoft secured a contract with the
U.S. military, outbidding Amazon’s offer (Forbes). While the contract has since not followed
through, this event serves as an example of the intense competition AWS experiences.
Threat of Existing Substitutes
Amazon’s online shopping platform allows for thousands of sellers to sell their products,
while also competing with Amazon’s own products. Consumers are able to directly compare
6
prices and competing products. Third party sellers also have an option to switch to direct-to-
consumer platforms, allowing them to avoid Amazon’s seller fees. Additionally, platforms such
as Ebay and Etsy may grant sellers higher profitability than what might be achieved on Amazon.
Power of Suppliers and Buyers
The nature of Amazon’s online marketplace has reduced its dependency on suppliers.
Their internal technological infrastructure allows them to be independent in this area as well. The
use of robots and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate processes in their fulfillment network
greatly benefits them. Thus, suppliers do not have high bargaining power. Conversely, buyers
have significant bargaining power. Specific to Amazon products, buyers are easily able to switch
and substitute to competing products. This occurs either directly on Amazon’s website or other
online selling platforms. Economic conditions can also create price sensitive buyers that might
demand more of a bargain. Amazon has an opportunity to reduce buyer power through
competitive pricing and product differentiation in quality.
Financial Statement Analysis
Weighted Average Cost of Capital
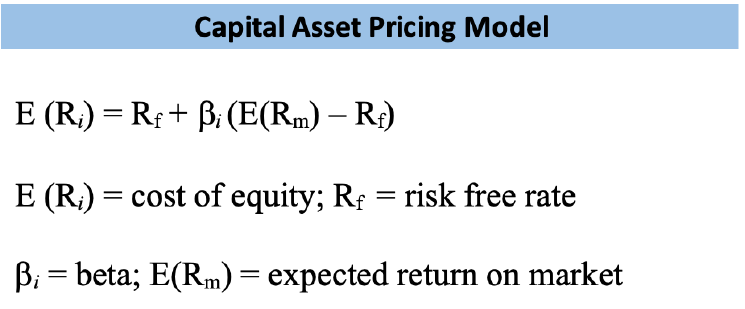
The Capital Asset Pricing Model is used to find the cost of equity This model is made up
of a few key components: the risk free rate, the market risk premium, and the company’s beta.
The following is the methodology used for each component.
7
Figure 1.1 - Capital Asset Pricing Model
The beta can be found by regressing Amazon’s returns against the market index’s returns.
Beta measures the riskiness of the stock in comparison to the market. A beta of 1.0 means that
the company’s stock performs in line with the market. A negative beta indicates that the
company’s stock moves in the opposite direction of how the market performs. A beta of 0 means
that the company has no correlation to the market. Since we are observing a publicly traded
company, we will be using the beta provided by Amazon of 1.17. This calculation uses the
monthly returns of the stock from the past five years. Amazon’s beta indicates to us that the
company’s individual stock is slightly more volatile than the market. When a company’s beta is
higher, we can expect its stock to have greater risk and potential for higher reward
(Investopedia).
Lastly, the risk-free rate is calculated using the yields of ten-year US treasury bonds.
These bonds have the most liquidity and have relatively no default risk, as we can trust the
ability of the US government to pay off contractual bonds. A 10-year long-term bond also
matching the term of the valuation period eliminates the reinvestment risk. The market risk
premium is found by using a five-year average of the S&P 500 monthly returns. This index
8
serves as our market observation representing the top 500 companies in the United States across
all leading industries.
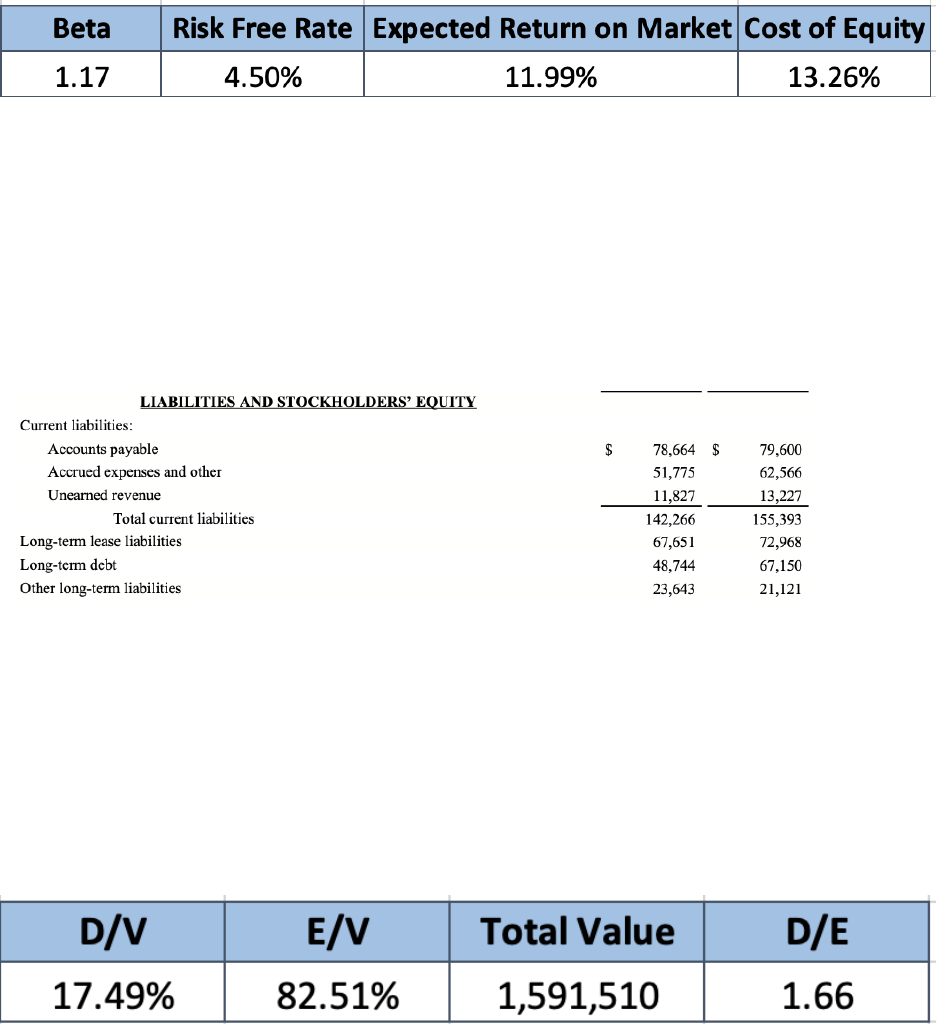
Based on these calculations, Amazon’s cost of equity is 13.26%. The cost of equity is
used later to calculate the weighted average cost of capital, or WACC.
Figure 1.2 - Capital Asset Pricing Model with Actuals
To find the cost of debt, we take the interest expense and divide it by the total debt. The
total debt is the sum of Long-Term Debt and Other Long-Term Liabilities from the Balance
Sheet (Appendix A), final amount of $278,360 million. The interest expense is found under the
2022 Statement of Operations.
Figure 1.3 - Amazon’s Liabilities from Balance Sheet 2022
To find the debt and equity weights for the capital structure, the total value of the firm
must first be calculated. The total value is the sum of total debt and market equity. Market equity
was found by multiplying the share price by the total shares outstanding as of December 31,
2022. The debt-to-value weight is 17.49% and the equity-to-value weight is 82.51%.
Figure 1.4 - Capital Structure Weights
9
The weighted average cost of capital multiplies the weights of debt and equity to the cost
of debt and equity. We find that the WACC is 10.99% and use this rate in our discounted cash
flow model.
Discounted Cash Flow Model
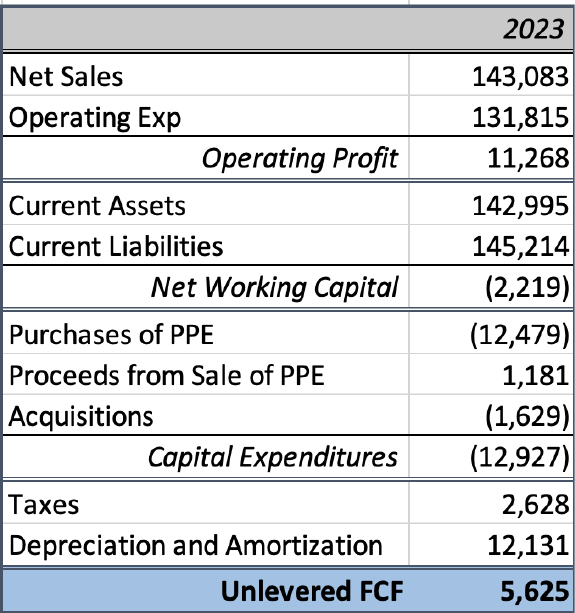
For this analysis, the model uses third quarter results and forecasts out the next 10 years.
The first part of the model is to identify the unlevered cash flow. Starting with total net sales,
operating expenses are deducted to get the operating profit. Both net sales and operating
expenses are found in the Statement of Operations. To calculate change in net working capital, it
is current assets less current liabilities, both found on the balance sheet. Cash paid for taxes,
depreciation, and amortization are all found in the statement of cash flows. Property, equipment,
and acquisitions are all found under the same statement, as well. The sum of these totals brings
us to our capital expenditures. The unlevered free cash flow is found by taking the operating
profit and deducting taxes. Adding back in depreciation and amortization, the change in net
working capital, and the change in capital expenditures. Our total free cash flow for 2023 is
$5,625 million.
10
Figure 1.5 - Unlevered free cash flow
To forecast the growth, estimates were taken from analysts at Yahoo Finance for net sales
growth. The estimated growth rate of operating expenses, net working capital, and capital
expenditures are 2% based on the Fed’s target inflation rate. The stable growth rate used in the
calculation of the terminal value incorporates a rate that is higher than the target inflation rate.
The terminal value is important in the discounted cash flow model as it sums up the infinite cash
flows beyond the forecasted period of this analysis. This terminal value is then added to the last
year of the 10-year forecasted free cash flows. The present value is taken of the total free cash
flows with the weighted average cost of capital as the discount rate. Based on the discounted
cash flow model, Amazon is estimated to generate $2,888,191 million rounded in free cash
flows, showcasing the company’s ability to add value for shareholders. In order to find the
intrinsic value of the stock, the present value of the future cash flows is divided by the number of
11
shares outstanding. This brings Amazon’s intrinsic share price to $279.59 per share. The share
price as of December 1, 2023 was at $147.03 per share, showing that the stock is currently
undervalued.
Sensitivity Analysis
Current growth estimates for Amazon appear a lot higher than expected for this company.
This is likely due to the net loss they experienced in 2022. As a result, the sensitivity analysis
utilizes estimates from another source analyst. These rates assume incremental sales growth in
the company over the next five years. With the different growth estimates, the present value of
free cash flows is $2,581,277 million rounded. Despite the variance in numbers, Amazon still
shows that it possesses the ability to add value that will create a return on investment for
shareholders. The intrinsic value in the sensitivity analysis was at $249.88 per share.
Financial Ratios
The use of financial ratios also allows for a quick comparison to industry standards.
Liquidity, solvency, efficiency, profitability, and market ratios were computed. Liquidity ratios
reveal to the investor the company’s ability to pay off their short-term debts. Solvency ratios
allow for an evaluation of the company’s debt compared to its assets and equity. Efficiency ratios
evaluate how effectively the company utilizes its assets and liabilities to generate a profit. The
profitability ratios demonstrate how well the company can earn a profit from its operations.
Lastly, the market ratios allow investors to make informed decisions on their investments by
predicting future performance of the company. Below are a few of the highlights that can have
the greatest impact on an investment (Investopedia).
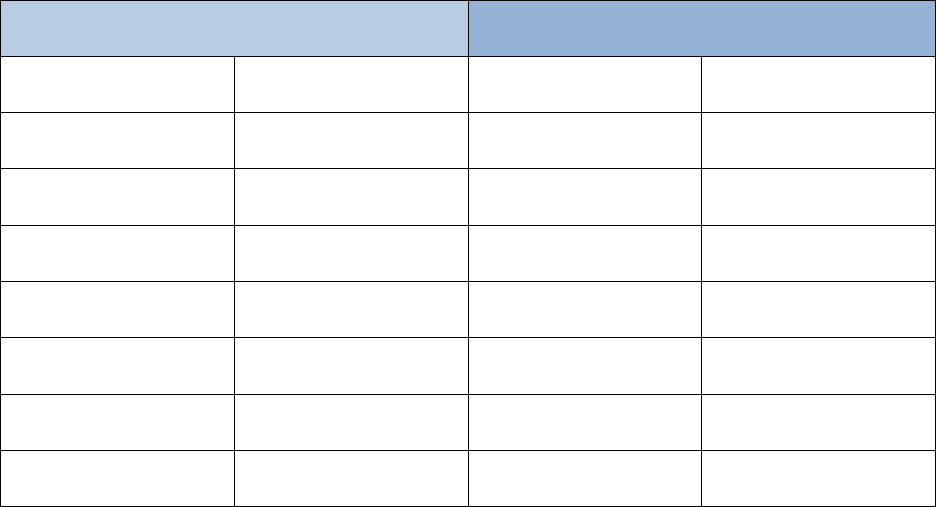
12
Sector Comparable
Amazon
Quick Ratio
0.36
Quick Ratio
0.74
D/E Ratio
0.77
D/E Ratio
1.66
PE Ratio
23.47
PE Ratio
66.32
PS Ratio
1.92
PS Ratio
3.24
PB Ratio
5.04
PB Ratio
7.18
Receivables Turnover
4.5
Receivables Turnover
3.29
Inventory Turnover
7.68
Inventory Turnover
5.99
Asset Turnover
0.81
Asset Turnover
0.83
Figure 1.7 & 1.8 - Consumer Cyclical Financial Ratios and Amazon Financial Ratios as of Q3 2023
Amazon ratios were calculated using the Q3 2023 Earnings Statement compared.
Comparables were calculated by CSIMarket, a financial media company that seeks to provide
analytical applications and financial information to the broader investment community. Within
the consumer cyclical sector, the quick ratio reveals that companies typically do not have enough
liquidity to pay short term liabilities. However, Amazon is well above the sector average closer
to 1, showing that it has greater capability to pay off short term liabilities. The debt-to-equity
ratio is a lot higher, indicating their operations are financed through borrowed money much more
than its comparable. The price-to-earnings ratio is greater for Amazon, likely due to investors
being willing to spend more on this company’s stock. Evidence is shown for this reasoning
through the discounted cash flow model, understanding that Amazon has great capability of
generating value for its shareholders.
Lastly, Amazon has a lower receivables and inventory turnover ratios. This could be
attributed to the nature of their e-commerce business. There is a huge variability in sales around
13
year-end due to holiday shopping, creating an increased use of credit card sales and longer
receivable cycles. Given the rapidly changing demand, there is also the challenge of accurately
and adequately stocking inventory. Amazon faces the issue of excessive stocking or weak sales
during lower consumer spending months compared to the industry.
Economic Analysis
Amazon’s stock price is volatile to changes in interest rates, labor market constraints,
among other key economic factors that affect their operations (Amazon 2022 Annual Report). It
is valuable to conduct an analysis to understand and measure the impact of the economy.
Investors can also use this analysis to best time buying, selling, or holding their investments that
will maximize their gain. It also allows for an outlook to better forecast and predict trends in
their stock valuation (RBC Global).
According to the St. Louis Federal Reserve, the phases of the business cycle can be
defined as follows. Expansion is when economic output increases, and contraction is when the
economic output declines. The normal state of the economy is expansion. Economic recovery is
the period that follows a recession, where output moves back to its pre-recession level. And
lastly, a recession is defined as the period between expansion and contraction (Federal Reserve
Bank of St. Louis). The National Bureau of Economic Research, or NBER, determines what
phase of the business cycle the United States economy is currently in. Many identify the phase
based on GDP, which the National Bureau of Economic Research does not solely rely on. NBER
makes the announcement of when a recession begins and ends, with a 6 to 24-month time lag.
The most recent announced recession was in February 2020 with the trough occurring in April
2020. NBER weighs a variety of economy-wide activity for their depth, diffusion, and duration
to understand the current phase of the cycle (NBER).
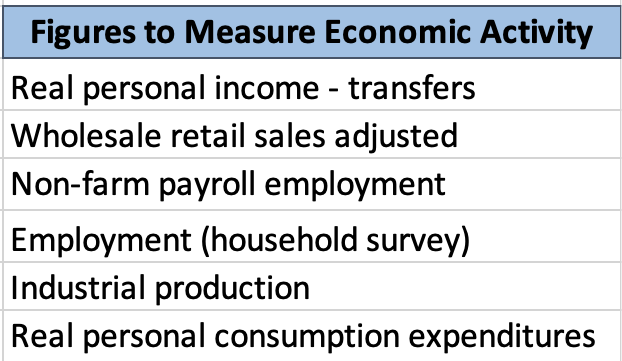
14
Figure 1.9 - NBER’s measures of economic activity
The Federal Reserve uses monetary policy as a tool to obtain three main goals: maximize
employment, keep prices stable, and moderate long term interest rates. They observe that
inflation can be low and stable at 2% per year. There are also labor market indicators such as the
unemployment rate, as well as those who are underemployed and discouraged workers. The Fed
also has two tools they use in adjusting monetary policy: the target for the federal funds rate and
various communications. When there is slow demand, it can be expected that unemployment
will rise and inflation will decline. This is associated with loose monetary policy through the
lowering of interest rates (Federal Reserve).
GDP Growth
While the NBER doesn’t solely look at GDP growth, it still holds indications on the
current stage of the economy. The US economy has experienced two straight fiscal quarters of
GDP growth in 2023, specifically the second and third quarter This is caused by the increase in
consumer, state and local government, and federal government spending. Housing, healthcare,
and financial services have been among the biggest service contributors to spending. There was
also an increase in nondurable goods spending, led primarily by prescription drugs (US Bureau
of Economic Analysis).
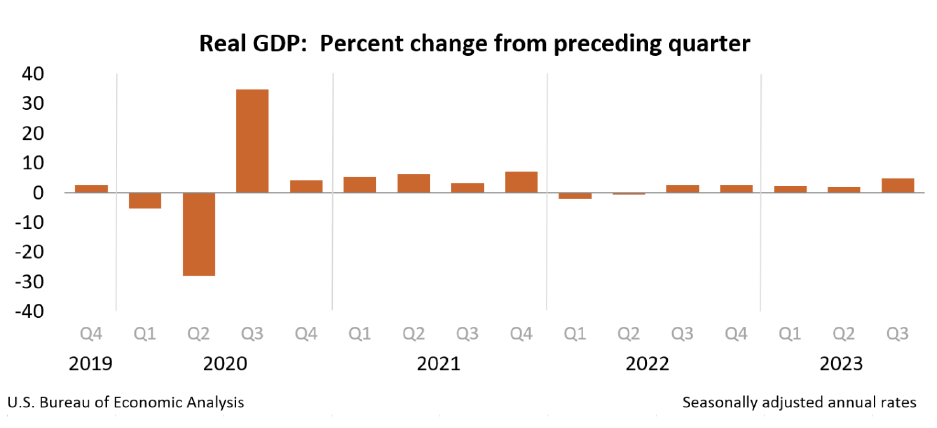
15
Figure 1.10 - Real GDP percent change from U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis
Inflation
Inflation is not a direct measurement of the state of the economy. However, it provides
great indication in expectation of consumer spending habits. In November 2022, items in the
consumer price index saw an increase of nearly 7.1% before seasonal adjustment. In November
2023, the consumer price index saw an increase of only 3.2%. While inflation continues to be
persistent, its effects are not as prominent for 2023 compared to 2022. Both households and
businesses looked for ways to minimize their costs. This is reflected through their purchases in
2022. The same trend does not continue for 2023, as there is still great spending in the economy
(Deloitte).
Interest Rates
To tame inflation, the Fed has enacted a tightening monetary policy. Over the course of
2023, we have seen approximately four major changes to the federal funds rate. Currently, the
effective federal funds rate (EFFR) sits at 5.33%. A higher rate should, in theory, create a lower
demand for spending and cause prices to decline. Interest rates in the banks will rise and make
16
borrowing more expensive. Corporate borrowing also begins to decrease for the same reason,
increasing their cost of capital. Historically, the Fed has kept interest rates lower around 2%
before the pandemic. This occurred during a period of economic expansion and encouraging
more spending to stimulate GDP growth (Federal Reserve Bank of New York).
Unemployment
There has been an extensive number of layoffs from technology companies this year, as
well as companies who experienced a boom during the pandemic. These layoffs are likely cuts in
expectation of slowed growth as the economy adjusts to normal levels. The current
unemployment rate sits at approximately 3.7%. Amid layoffs and threats of layoffs, the labor
market remains strong for 2023. There are current worries that skilled personnel will be exiting
the workforce in the next ten years. With many opting for earlier retirement and not enough
flexibility in benefits to retain them. As many are exiting, jobs are continuing to be added as the
next generation seeks employment (Deloitte).
State of Economy
Based on the above criteria, there is strong evidence that the US economy is in recovery
from the 2020 recession. Recessionary fears have been sparked by recent layoffs and increased
prices, but many analysts forecast an optimistic outlook for the economy. There is the potential
that the Fed may raise rates once again, pushing some areas closer to financial crisis. However,
these rates would only be raised if inflation continues to rise. Stock prices are expected to drop
during a recession, which can be of benefit for potential investors in Amazon’s stock. This will
create an opportunity to purchase a share at a lower cost, allowing it to grow in value as the
economy recovers and Amazon continues to grow (Nasdaq).
17
Macroeconomic Risks
The change in interest rates posed by the Fed can affect Amazon’s stock price. Lower
interest rates can increase consumer spending, making equities more attractive. Amazon states
that their stock price fluctuates significantly to a change in interest rates. Interest rates will also
affect the cost of their corporate borrowing.
Amazon also cites that consumer recessionary fears will make it difficult to forecast
consumer spending patterns. This currently impacts the North American segments and similar
expectations can affect the International segment as well (Amazon 2022 Annual Report).
Demand will return to a more seasonal pattern than what was previously observed during the
pandemic. Amid the pandemic, Amazon expanded their employment to keep up with massive
demand. As sales continue to slow down to normal expectations, the cost of labor has continued
to increase. There have been about 27,000 layoffs in the company to reduce these costs (AP
News). Additionally, there has been a reduction in projects that are no longer forecasted to
sustain revenues needed to exceed expenses. However, such strategic moves have well
positioned Amazon in the event the economy is in recession.
Inflation also affects both Amazon and their customers. Rising inflation has created
increased operational costs, which creates a reduction in their free cash flows. Revenue will be
largely affected in AWS with business customers choosing to optimize their costs.
18
Review of Company
Evaluation of Management
There is no denying the fact that Amazon has grown to be one of the largest and most
influential companies in the world. In the history of Amazon, there has only been two Chief
Executive Officers: Jeff Bezos and Andrew Jassy. As mentioned previously, Bezos was the
founder of this billion-dollar enterprise and served as CEO for nearly three decades. Previously
Time magazine’s 1999 person of the year, he managed to pioneer and kickstart Amazon into a
rapid growth that was unprecedented. The company mission of being the most customer centric
company in the world sat at the forefront of his decisions. This being reflected in the company
culture that was built, consistently focused on innovation that would serve the customer.
However, Bezos announced in 2021 that he would be stepping down, looking to still remain on
the Board of Directors but with hope to pursue different ventures. Andy Jassy, current President
and CEO of Amazon, filled in Bezos’s shoes in July of 2021 (Frontline PBS).
Jassy first joined Amazon in 1997 and has held multiple leadership positions with focuses
on delivering both to the business and the customers. He is most notable for founding AWS,
which came to be the largest revenue earner for Amazon to date. He served as the CEO for AWS
from 2016 to 2021. Entering his new role brought on immediate challenges with slowed growth
following the aftermath of the global pandemic and contracting economic expectations.
However, his tenure with Amazon would prove most valuable in executing their company
strategy (Frontline PBS).
In 2022, investors were bringing pressure to Jassy on increasing profitability. One of the
focuses was to decrease dependability on AWS covering revenue shortfalls in the other
segments. There was a push for the North American and International segments to increase their
19
profit margin. Jassy has also since executed a variety of tactics to drastically cut expenses.
Amazon made around 27,000 layoffs and froze corporate hiring that year (AP News). They also
scaled back on projects that were underperforming, such as healthcare and grocery. One of the
biggest changes that proved to be beneficial was reorganizing the fulfillment center. Rather than
utilizing a national network, it was split up into eight main regions that span across the states.
Each main fulfillment center would focus on smaller geographic areas, holding select inventory
that meets the demands of that demographic (Amazon 2022 Annual Report).
Executive compensation is structured in a way that incentivizes the CEO to operate and
think about long-term, sustainable growth. The CEO is rewarded time-vested restricted stock as a
way to drive commitment for strong and long term returns to shareholders. Jassy did not receive
any equity grants in 2022 (Amazon 2023 Annual Report). This encourages a dedication to
continuous innovation in the business, guiding the company in a direction that will bring positive
gain for the shareholders. Other arrangements of executive compensation might allow the CEO
to continuously be rewarded despite having a declining stock value.
Key Risks
Given the large size of Amazon as a company, there are numerous risks that can affect
their stock performance and overall profitability. For the sake of this analysis, operational and
business risks will be discussed at each major segment. Amazon is operationally split between
AWS, North America, and International segments. The mentioned risks are also not a definitive
list of what the company faces. See the economic analysis section for risks related to
macroeconomic conditions.
20
North American Segment Risks
There is a huge variability in sales that Amazon faces towards the end of the year. This is
primarily due to the holiday season causing a disproportionate increase in consumer spending.
Failure to maintain the necessary inventory to meet such high demand could reduce profitability.
This stock of inventory needs to be adequate in quantity and accurate in the most sought-after
categories. Overstocking less popular areas will require various markdowns.
A related risk to inventory is a failure to successfully operate in fulfillment centers. The
nature of the Prime membership benefits has created a facility that is fast paced and high
pressure. In addition, there are third party sellers who pay a premium to use Amazon’s shipping
and fulfillment logistics. All inventory needs to be tracked, well managed, and delivered to the
customer in a quick turnaround to upkeep the reputation of the Prime benefits. Each region gets a
never-ending influx of orders on the daily. It requires adequate staffing, possessing the ability to
work efficiently in these conditions. There are current labor market constraints, causing an
increase in their payroll costs. Amazon also relies on a limited number of shipping companies in
their fulfillment process. Both staffing issues and performance issues can be very costly
(Amazon 2022 Annual Report).
International Segment Risks
The international segment is at risk for multiple global factors. The first being foreign
exchange risk. There are multiple emerging markets that Amazon has invested its operations in
where foreign currency fluctuations are heavily prevalent. If the US dollar strengthens,
marketable securities that are held in British Pounds, Canadian Dollars, Euros, and Japanese Yen
may be worth less than expected. Emerging markets may also not establish the proper
infrastructure that meets the metrics and standards observed in the North American segment.
21
Cultural and language barriers can keep Amazon from operating with an efficiency that will
bring expansive growth. There are also different labor laws that they have to follow. Another risk
the international segment faces is lower levels of internet usage among consumers. The majority
of their sales are driven by Internet use, directly translating into profitability. In relation, there is
an expected lower level of consumer spending in emerging markets. The varying levels of
economic welfare for developing countries may cause slower revenue growth than what can be
achieved in the North American segment (Amazon 2022 Annual Report).
AWS Risks
One of the major risks that AWS faces is their choice in expansion with large language
models and generative AI. While these projects pose a hopeful avenue for more revenue, it will
require a larger quantity of capital expenditures up front. The timing, effectiveness, efficiency,
and costs all create risk to the operating results of AWS. Business customers may not adopt new
product or service offerings immediately. Monetization could also be low if initial expectations
from customers are not met. Currently, AWS is in competition with AI products launched from
Google and Microsoft. Competitors may adopt more aggressive pricing that is lower than what
AWS currently offers. Other companies may also possess the ability to devote more resources
into developing infrastructure or technology. Additionally, competitors can have a long-standing
history with business customers, maintaining brand loyalty among them with current product
offerings (Amazon 2022 Annual Report).
Legal Risks
Amazon is currently in an open investigation with the Federal Trade Commission over a
violation of antitrust laws as of 2023. The claim is that Amazon uses their vast power in an
anticompetitive way, allowing them to operate like a monopoly. Complaints have alleged that
22
current competitors are kept from growing and new entrants are kept from entering the market.
More specifically, the conduct is claimed to occur in the online marketplace for both consumers
and sellers (U.S. Federal Trade Commission). There is no projected date for when a ruling might
come into effect. Similar cases have occurred recently in Amazon’s International segment in the
European Union. The EU cases ended in a settlement with Amazon creating a list of various
compliances with the EU’s anti-competitive laws. This serves as an example of the kind of
actions the company might need to take assuming the current American investigation is
unfavorable for them. The required actions can affect their profitability, how they manage
relationships with third-party sellers, and negatively impact consumers.
Conclusion
Investment Recommendation
Through this analysis, it is strongly recommended that AMZN is a buy. The current share
price is approximately $100 under its intrinsic value. Purchasing the stock at a lower share price
could bring an opportunity for the investor to sell it at a higher price in the future. The company
also has a large ability to add value for shareholders through its operations. New lines of
business are strategically thought out. These new initiatives maintain the ability to minimize
losses if they are not successful. If they are successful, these initiatives such as Amazon’s
advertising services, would produce another stream of revenue. Both AWS and the North
American segment have strong project growth for the future, as dependency on technology
continues to increase. While there are various risk factors, the company is well positioned to
stand strong against various headwinds. For these reasons, shares in Amazon would provide a
great return on investment.

23
Works Cited
Ahn, Hie Joo, and Chad Fulton. “Index of Common Inflation Expectations.” The Fed - Index of
Common Inflation Expectations, 9 Feb. 2020,
www.federalreserve.gov/econres/notes/feds-notes/index-of-common-inflation-
expectations-20200902.html.
Allen, Bruce. “Economic Indicators That Help Predict Market Trends.” Investopedia,
Investopedia, 31 Mar. 2024, www.investopedia.com/articles/economics/08/leading-
economic-indicators.asp.
"Amazon." Amazon.com Announces Third Quarter Results. Amazon, 26 October 2023. Amazon
Investor Relations, https://ir.aboutamazon.com/quarterly-results/default.aspx
“Antitrust: Commission Opens Investigation into Possible Anti-Competitive Conduct of
Amazon.” European Commission - European Commission, 17 July 2019,
ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/pl/ip_19_4291.
“Amazon 2022 Annual Report" Ir.aboutamazon. Amazon, 2023,
https://ir.aboutamazon.com/annual-reports-proxies-and-shareholder-letters/default.aspx
“Amazon Empire: The Rise and Reign of Jeff Bezos (Full Documentary) | Frontline.” YouTube,
Frontline PBS, 19 Feb. 2020,
www.youtube.com/watch?v=RVVfJVj5z8s&ab_channel=FRONTLINEPBS%7COfficial
.

24
Bloomenthal, Andrew. “Financial Ratio Analysis: Definition, Types, Examples, and How to
Use.” Investopedia, Investopedia, 26 Feb. 2024,
www.investopedia.com/terms/r/ratioanalysis.asp.
Bugembe, Mike. “Grow or Die the New Reality of Ecommerce.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 16
May 2022, www.forbes.com/sites/mikebugembe/2022/05/06/grow-or-die-the-new-
reality-of-ecommerce/?sh=4dfa36a03fb1.
“Business Cycle Dating.” NBER, www.nber.org/research/business-cycle-dating. Accessed 14
Dec. 2023.
“The Business Cycle - the Economic Lowdown Podcast Series.” Saint Louis Fed Eagle, Federal
Reserve Bank of St. Louis, 25 Apr. 2023, www.stlouisfed.org/education/economic-
lowdown-podcast-series/episode-18-the-business-cycle.
“Consumer Discretionary Sector Financial Strength Information.” Consumer Discretionary
Sector Financial Strength, from the Q3 2023 to 3 Q 2022, Leverage, Interest, Debt
Coverage and Quick Ratios,
csimarket.com/Industry/industry_Financial_Strength_Ratios.php?s=400. Accessed 14
Dec. 2023.
Carpenter, J. William. “Who Are Alibaba’s Main Competitors?” Investopedia, Investopedia, 11
Sept. 2022, www.investopedia.com/articles/markets/042716/baba-who-are-alibabas-
main-competitors.asp.
“Effective Federal Funds Rate.” Effective Federal Funds Rate - FEDERAL RESERVE BANK of
NEW YORK, www.newyorkfed.org/markets/reference-rates/effr. Accessed 14 Dec. 2023.

25
Hadero, Haleluya. “Amazon Cuts 9,000 More Jobs, Bringing 2023 Total to 27,000.” AP News,
AP News, 20 Mar. 2023, apnews.com/article/amazon-layoffs-jobs-cuts-jassy-
0e857f39702de134c8f677c5b5731688.
Hadero, Haleluya. “FTC Faces Long and Winding Road Ahead in Amazon Antitrust Lawsuit.”
PBS, Public Broadcasting Service, 10 Oct. 2023, www.pbs.org/newshour/politics/ftc-
faces-long-and-winding-road-ahead-in-amazon-antitrust-lawsuit.
Holland, D.A. (2018), An Improved Method for Valuing Mature Companies and Estimating
Terminal Value. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 30: 70-77.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jacf.12279
Liberto, Daniel. “What Beta Means When Considering a Stock’s Risk.” Investopedia,
Investopedia, 11 Jan. 2024, www.investopedia.com/investing/beta-know-risk/.
“News Release.” Gross Domestic Product, Third Quarter 2023 (Advance Estimate) | U.S.
Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), 2023, www.bea.gov/news/2023/gross-domestic-
product-third-quarter-2023-advance-estimate.
“Research Guides: Porter’s Five Forces Analysis: Power of Suppliers.” Power of Suppliers -
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis - Research Guides at Baruch College,
guides.newman.baruch.cuny.edu/c.php?g=188285&p=1244256#:~:text=The%20Power%
20of%20Suppliers.,or%20lack%20of%20alternative%20sources. Accessed 14 Dec. 2023.
Ritchie, John Newman & Amy, and Nick Jones. “FTC Sues Amazon for Illegally Maintaining
Monopoly Power.” Federal Trade Commission, 5 Dec. 2023, www.ftc.gov/news-

26
events/news/press-releases/2023/09/ftc-sues-amazon-illegally-maintaining-monopoly-
power.
Ronald E. Shrieves & John M. Wachowicz Jr. (2001) Free Cash Flow (FCF), Economic Value
Added (EVA), and Net Present Value (NPV):. A Reconciliation of Variations of
Discounted-Cash-Flow (DCF) Valuation, The Engineering Economist, 46:1, 33-52, DOI:
10.1080/00137910108967561
“The Five Forces.” The Five Forces - Institute For Strategy And Competitiveness - Harvard
Business School, www.isc.hbs.edu/strategy/business-strategy/Pages/the-five-forces.aspx.
Accessed 15 Apr. 2024.
“United States Economic Forecast.” Deloitte Insights, Deloitte, 16 Oct. 2023,
www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/economy/us-economic-forecast/united-states-outlook-
analysis.html.
“Useful Definitions.” Economic Policy Institute, www.epi.org/newsroom/useful_definitions/.
Accessed 14 Dec. 2023.
Walsh, Joe. “Pentagon Scraps Microsoft’s $10 Billion Cloud Computing Deal after Lawsuit from
Amazon.” Forbes, Forbes Magazine, 6 July 2021,
www.forbes.com/sites/joewalsh/2021/07/06/pentagon-scraps-microsofts-10-billion-
cloud-computing-deal-after-lawsuit-from-amazon/?sh=372a538f243b.
“What’s the Relationship between the Stock Market and the Economy?” RBC Global Asset
Management, www.rbcgam.com/en/ca/learn-plan/investment-basics/whats-the-
relationship-between-the-stock-market-and-the-economy/detail. Accessed 15 Apr. 2024.

27
"Yahoo Finance." Historical Data. Yahoo, 14 December 2023. Yahoo Finance,
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/AMZN/history?p=AMZN
"Yahoo Finance." Profile. Yahoo, 14 December 2023. Yahoo Finance,
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/AMZN/profile?p=AMZN
"Yahoo Finance." Statistics. Yahoo, 14 December 2023. Yahoo Finance,
https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/AMZN/key-statistics?p=AMZN
